
Wireless power transfer (WPT) is a system for wirelessly charging the batteries in electric vehicles. There are two main methods:
stationary WPT
dynamic WPT
With stationary charging, the electric energy is transferred to a parked vehicle. In dynamic wireless charging systems, the energy is transferred via a special driving lane equipped with a primary coil system at a high power level to a secondary coil of a moving vehicle. Because the range of most EVs is now good, the need for dynamic charging has reduced. I will, therefore, concentrate on static or stationary WPT.
To wirelessly charge, a suitably equipped electric vehicle simply parks over an induction pad and charging commences automatically. Just like with wired connections, the rate of charge is set from within the vehicle. There are no visible wires or connections. A primary charging pad is buried or set on the ground (on a drive or in a garage for example) and a secondary pad is integrated onto the vehicle.
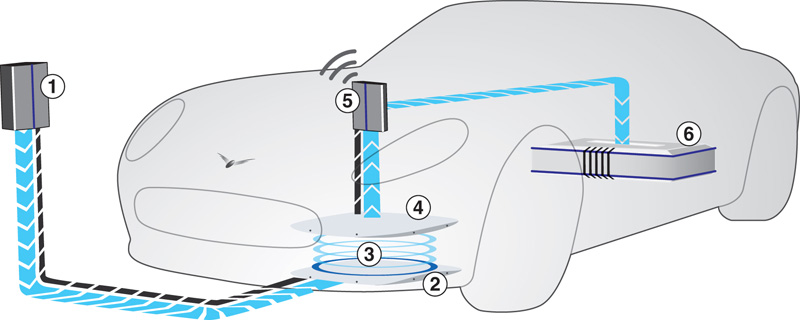
The power supply (Fig.1) takes a mains voltage input and produces high-frequency current (>20 kHz). Its output current is controlled and applied to the primary pad.
Power is transferred from the primary pad to the secondary pad using transformer action. The onboard charger takes power from the receiver pad and provides a controlled output to the battery. The controller is required to provide an output that remains independent of the load and the separation between pads.
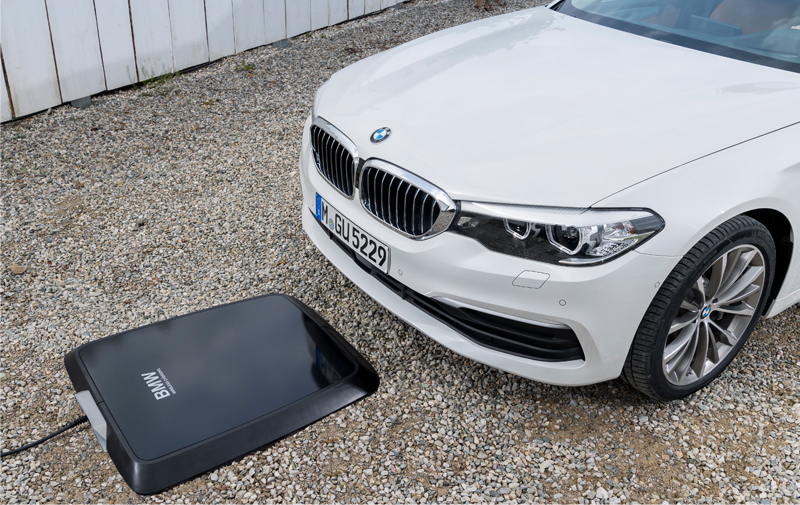

BMW has developed a wireless charging system. As soon as the vehicle has been parked in the correct position above the inductive charging station (Fig.2), a simple push of the Stop/Start button, starts the charging process. Once the battery is fully charged, the system switches off automatically just as if it was plugged in.
The system helps the driver to manoeuvre the car into the correct parking position with the help of a Wi-Fi connection between the charging station and vehicle. An overhead view of the car and its surroundings is displayed in the centre control display. Coloured lines help guide the driver into the correct spot. A graphic icon shows when the correct parking position for inductive charging has been reached. This can deviate from the optimum position by up to 7 cm longitudinally and up to 14 cm laterally.
The contactless transfer of energy between the GroundPad and CarPad is conducted over a vertical distance of around 7.5 cm. The GroundPad generates a magnetic field. This induces a voltage in the CarPad, which then causes a current flow to the onboard charger (just as if the car was plugged in).
WPT is designed for slow charging so is ideal for home chargers where, for example, you simply park the vehicle as normal and charging automatically takes place overnight.









