Brembo highlights the best approach to caliper maintenance, and some of the products that may help you along the way.
When a car’s braking system begins to emit loud screeching or grinding noises, or experiences a reduction in the quality of performance, it is most commonly thought to be due to faulty brake pads or discs. This, however, is not necessarily always the case. The brake calipers can also be the source of braking issues. Luckily, carrying out appropriate maintenance is often enough to ensure their smooth performance.
Let’s take a look at the common reasons for braking component deterioration and the maintenance options available that help to preserve optimum braking functionality.
The foremost vehicle safety feature
A braking system is one of the most vital aspects of a vehicle, with the brakes regularly applied and released.
When pressure is applied to the brake pedal, the master cylinder forces brake fluid through the hydraulic lines. The pressure generated by this action is immediately transferred to the brake calipers, which, with the additional help of large pistons housed inside them, force the pads into contact with the brake disc, stopping or slowing the vehicle.
Common problems
For a braking system to work both correctly and safely, the components need to be able to move freely. As brake calipers are made from metal, they have a tendenccy to corrode and deteriorate over time.
Corrosion inhibits the movement of braking components. For example, this can prevent the brake discs and pads from retracting the necessary amount of distance, which can result in constant light contact between both components. In the long run, this can lead to irregular component wear, overheating of the system as well as noise and vibrations.
The causes of corrosion are numerous and go well beyond just water. Pollution, salt, dirt and constant stress on the braking system all accelerate its spread. A high-pressure water jet used during car washing, for instance, can blast off the protective seals from the calipers, creating water seepage between the sliding surfaces. What’s more, alkaline detergents used for car washing can lead to corrosion and oxidation, with unwelcome brake squealing a likely outcome.

How to avoid them
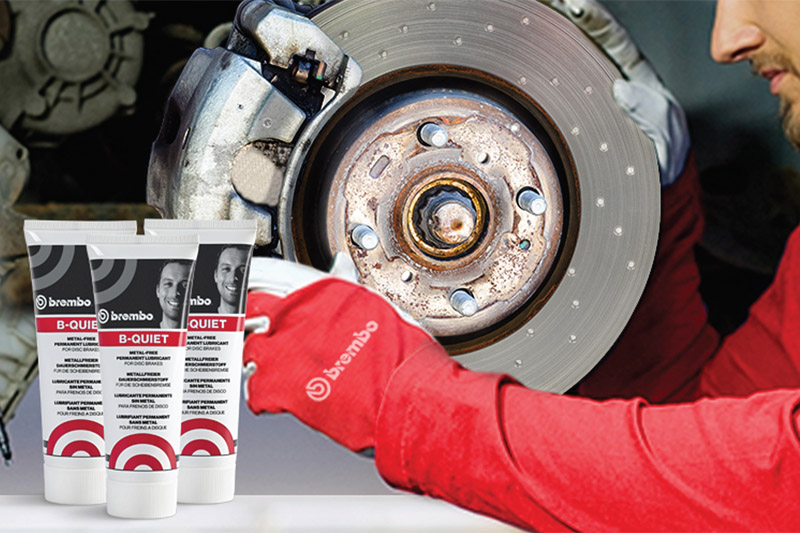
Suitable caliper maintenance entails a series of tasks and checks that ensure the component remains fully efficient. Dedicated lubricants – of which there are separate types for different caliper components – and the use of caliper repair kits form the two main bases of how caliper maintenance is successfully performed.
Lubricants
When carrying out maintenance, the selection of the right lubricant is of utmost importance in ensuring the correct functioning of a braking system. Use of an unsuitable lubricant is highly problematic, potentially resulting in greasy caliper guides which can become acidic. When this occurs, the bracket can suffer from a loss of mobility, which can lead to the overheating of the brakes.
The type of lubricant used during maintenance depends on the contact surface that needs to be treated. Exposed points of contact, such as the resting points on the supports and calipers require a lubricant that not only must be able to withstand the high temperatures generated by braking, but also be resistant enough to avoid being washed off by water.
Brembo B-Quiet ticks all of these boxes. Moreover, unlike copper-based lubricants, it is completely metal-free, providing a further bulwark against galvanic oxidation. This type of lubricant can be effectively applied to the resting points between the metallic parts of the brake pad and the caliper. During application, however, it is of utmost importance that the lubricant be kept away from the friction surface of the brake pads and discs, as this could compromise braking performance.
The sliding guides of a floating caliper and the related pins require a different type of lubricant. The rubber parts of the brake caliper (protective seals, dust covers, caps and sliding pin rubber boots) are produced using EPDM, a material which is compatible with DOT brake fluids. EPDM requires a specific lubricant compatible with this material.
How to correctly perform caliper maintenance
- Inspect and clean the springs and the caliper bracket, then clean the pad seats thoroughly
- Lubricate the contact points between the brake pad and the caliper with a dedicated lubricant such as Brembo B-Quiet
- Check the pistons, seals, covers and caliper sliding components, to make sure they are free of damage and corrosion and that they slide smoothly. It is also advisable to check that there are no leaks
- Clean and lubricate the caliper sliding pins with a dedicated lubricant compatible with EPDM rubber
- Use specific grease for each component
- In the event of damaged, corroded or bent components, replace them with Brembo’s brake caliper repair kit
Caliper repair kits
Brake calipers feature some internal parts that can wear and deteriorate over time. This is due to normal sliding friction, which as a result of issues such as the weather and the presence of salt and chemical agents on the roads, can result in the corrosion of the rubber and metallic parts of the calipers.
When one or more of the caliper’s components has become worn or deteriorated, the issue can easily be remedied by using a caliper repair kit. This consists of caliper components that are most subjected to wear, such as sliding pins on floating calipers, dust seals, piston seals and the pistons themselves, as well as the necessary lubricant for each component such as silicone grease.