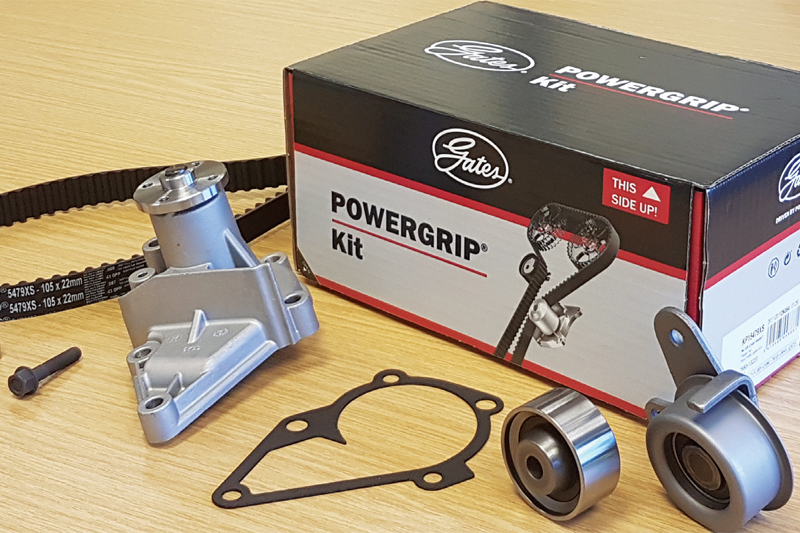
In this investigation, the Gates technical team identifies the primary causes of premature failure of the guide pulley bearings in specific timing belt drive systems soon after replacement.
Vehicle information
Models: Kia (Rio, Cerato) Hyundai (Accent, Getz, Matrix, Coupe)
Engines: 1.4L, 1.5L and 1.6L petrol
Year: 1996–2014
When the guide pulleys in the timing belt drive systems on Kia and Hyundai models with similar engines were reported as failing prematurely after replacement, the Gates technical team launched an investigation. The models affected were in the 1.4L, 1.5L and 1.6L range, and the pulleys were part of both the Gates PowerGrip K015479XS and the Gates Powergrip Plus Water Pump Kits KP15479XS.
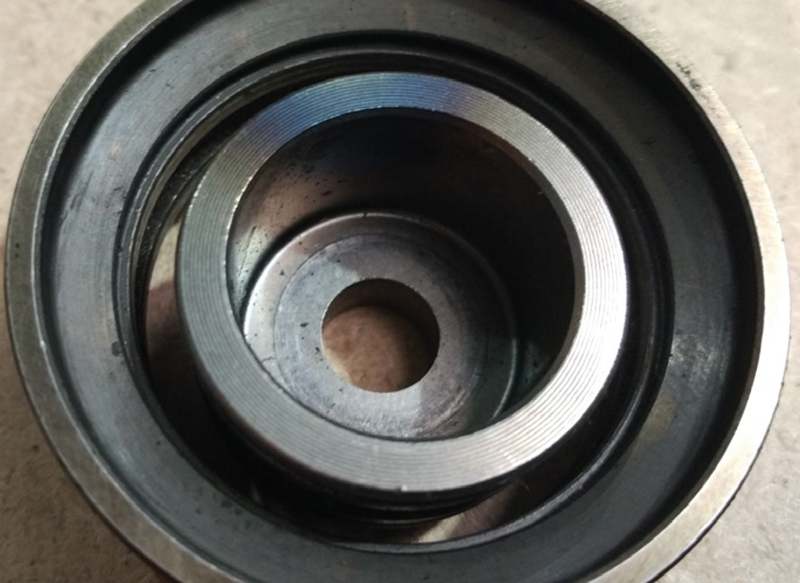
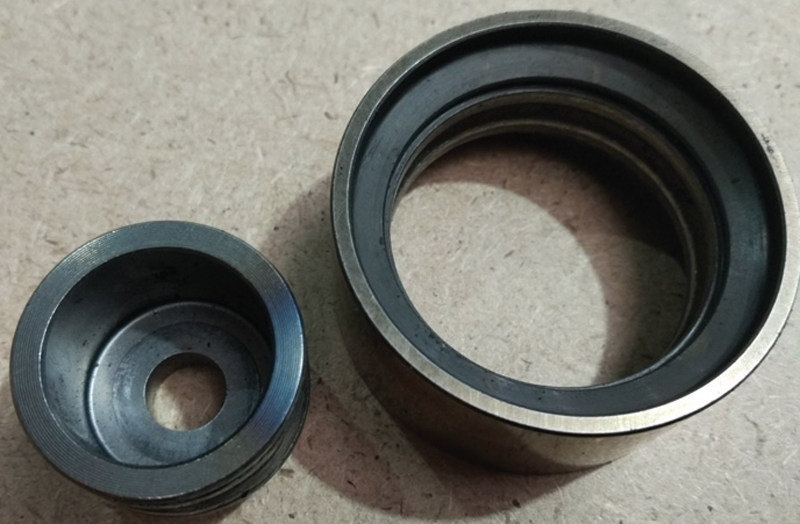
The investigation revealed that, in most of the cases, the failure was due to the guide pulley bearings failing, causing belt damage, loss of synchronization and subsequent damage to the components of the timing mechanism. In the process, the pulleys came apart and the inner ring often became detached from the outer ring.
In all of the cases examined, there were traces of overheating to the guide rollers and scuffs on the back surfaces of the belts along the entire length. Typically, scuffs were found around the working surface of the tensioner pulley, too.

Fault diagnosis
During installation, the initial belt tension is provided by the force of a spring (not included in the kits). The spring rests with one end on the engine structural element, while the other end sits on a special lug located on the tensioner bracket. After tension adjustment and after securing the tensioner with two bolts, it remains fixed. The spring is not actually involved in the operation of the drive.
Replacement of the spring is not typically prescribed by the car manufacturer if there is no visible damage. However, it is good workshop practice to replace the spring when overhauling all the other parts in the drive, even though OE does not prescribe it. That spring has been in the same position for four or five years and there are a number of issues that could lead to problems
Over time, the spring’s characteristics begin to decline. If the fixing bolts are incorrectly torqued, the spring might jump over the lip, causing the spring to rest directly on the pulley after the installation procedure – rather than on the tensioner lug. It could then begin to rub against the pulley during engine operation generating a serious amount of friction as well as causing mechanical damage to the pulley.

The friction generates an enormous amount of heat. Once the heat is transferred to the belt, the guide pulley heats up, causing the bearing to overheat and the lubricant to leak out. The overall consequence is even more heat generation on the bearing, with overloading and eventual destruction.
Investigation recommendations
In any replacement or installation situation, it is important to observe both the correct relative positioning of all the elements of the tensioning mechanism, and the sequence for tightening the fixing bolts. Applying the prescribed torque is essential.
A key investigation finding was the importance of observing the correct position of the spring, which must not rest on the pulley.
There are some more general lessons to be learned, too. When making the diagnosis, it is crucial to pay attention to the single element of the drive system that has visible damage, but also to consider the condition of the entire system and each individual element.

Online guidance
Online digital instructions are available for all Gates PowerGrip Kits. They are engine specific and include drive system layouts. They are accessed via a QR Code or the Product Key on the side of each box.