Melett takes a look at the causes of turbo oil leaks, and offers some practical advice for preventing them.
What are oil leaks?
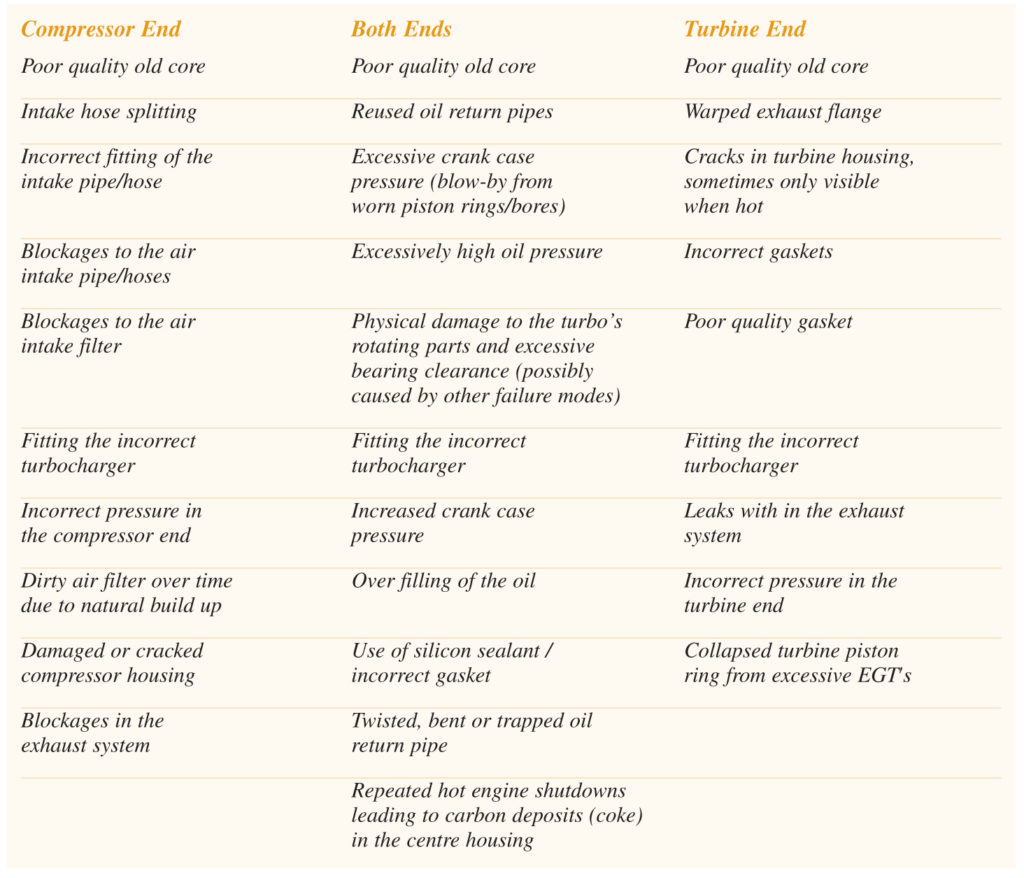
Oil leaks can be caused by a variety of factors – the main factor being incorrect pressure within the compressor and turbine housings. Oil leaks can cause catastrophic damage to the bearing systems and occur within seconds of the turbocharger commencing operation. When a turbocharger is installed correctly, it should NOT leak oil. However, there can be cases where oil leaks occur. The table on the right highlights some of the main causes and signs of oil leaks.
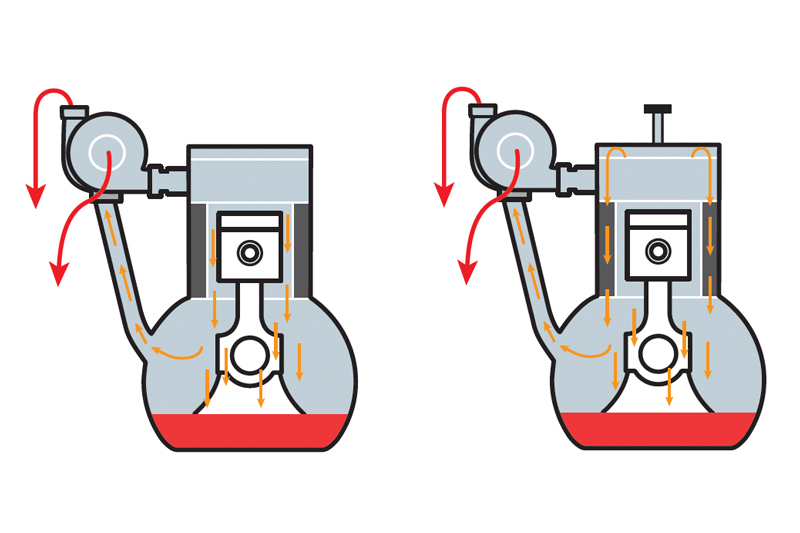
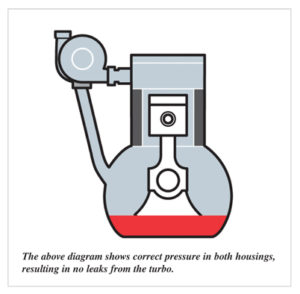
Example of correct pressures:
PLEASE NOTE:
An oil leak can also occur when engines are running on idle. The pressure within the housings is lower, which in turn can lead to a vacuum being created, causing the oil to leak into the turbine housing. Once the engine starts to run at normal speeds, the pressures will be restored and the leaks will stop.
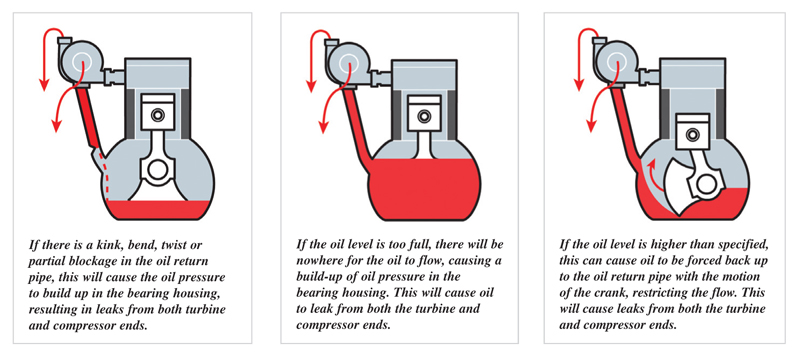
Causes of oil leaks
Examples of how oil leaks can occur:
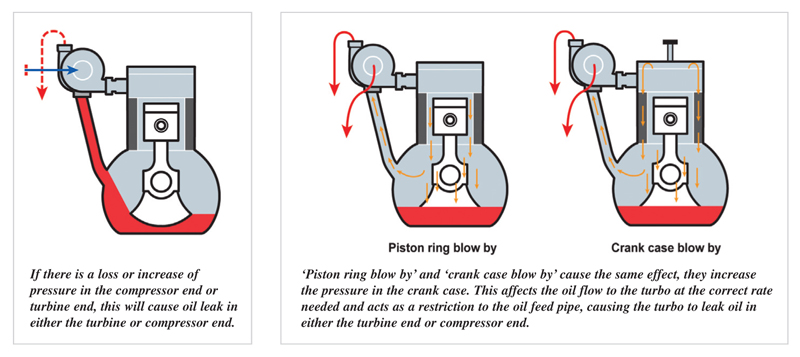
PLEASE NOTE:
Oil leaks can occur on VSR (high speed) balancing machines as the ambient pressures required to create the seal are not present as no housings are used. This can then force out oil from both the compressor end and turbine end, giving the impression of a leak. This is unlikely to occur when the replacement turbo is fitted to the engine.
‘Piston ring blow by’ and ‘crank case blow by’ cause the same effect, they increase the pressure in the crank case. This affects the oil flow to the turbo at the correct rate needed and acts as a restriction to the oil feed pipe, causing the turbo to leak oil in either the turbine end or compressor end.
Preventing future oil leaks:
■ Ensure air and oil drain systems are clear from blockages or restrictions
■ Check the exhaust system to make sure there are no leaks present
■ Do not use silicone on oil gaskets as it can easily become detached and block oil passages Ensure DPF and Catalytic converter are free of blockages
■ Use the correct gaskets and o-rings
■ Only use the correct standard of turbine housings and compressor housings
■ Check for correct oil levels and pressure