Dayco provides some information on a piece of technology developed specifically for start-stop engines.
Although, with the rise of electrical propulsion systems, it may seem that the days of the internal combustion engine are drawing to a close, in the workshop, it’s still traditionally powered vehicles fuelled by petrol or diesel that dominate the service bay.
That doesn’t mean, however, that ICE technology hasn’t developed, because despite the ageing car parc, many of the vehicles that technicians work on daily have at the very least a start-stop function, which must be serviced using the correct replacement components.
The development of this technology shouldn’t be dismissed because the vehicle manufacturers have relied on component suppliers such as Dayco, to come up with the required solutions and deliver effective startstop systems that work seamlessly.
Although initially, some VMs opted for uprated starter motors to cater for the greater number of engine starts these vehicles need, the starter/alternator solution has proved to be most satisfactory.
Faster, quieter start
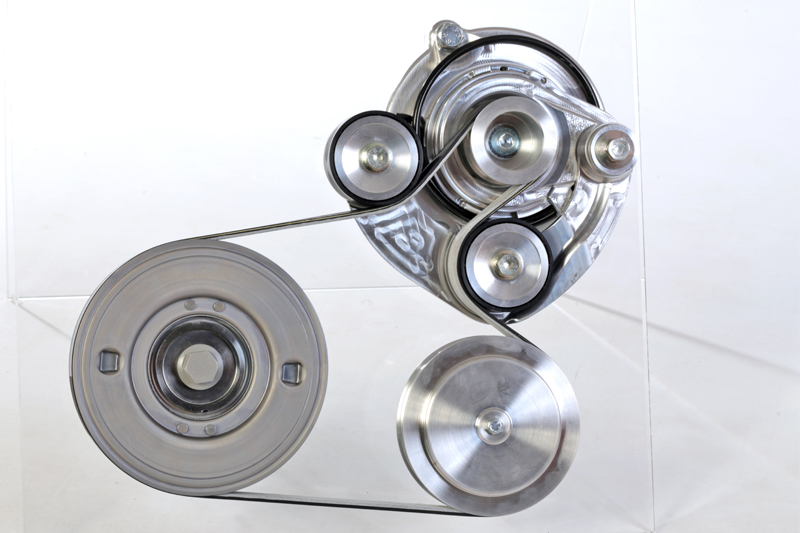
The starter/alternator combines both a starter motor and an alternator into one component, which is able to switch between each function on demand and, driven by a belt, it provides a faster, quieter engine start. The combination is now referred to as belt starter generator or BSG.
The two primary challenges with a BSG system are to engineer an auxiliary belt with the strength to start the engine, but still drive the alternator and related components like the power steering pump and air conditioning compressor etc, while still being no wider than a standard auxiliary belt.
Despite the difficulty in achieving this objective, by applying its technical knowledge, Dayco designed and developed not only a revolutionary belt of a traditional width, but also coupled it with a patented self tensioning system able to maintain the correct tension on the belt to allow power to be transmitted in either direction, depending on whether starting the engine or driving the ancillary components.
In contrast to a conventional auxiliary drive system, the belt needs to withstand forces in both directions, which calls for different technology and manufacturing processes. When it comes to maintaining the correct tension on the belt, the STS maintains a balanced tension on both sides of the belt in relation to the BSG drive pulley. Instead of having a tensioner on just one side of the belt system, the tensioning device connects both sides of the BSG.
The Dayco STS is designed to create a balance of forces between the two sides at all times, which enables the BSG to seamlessly switch between its starting and charging modes to allow the vehicle’s start-stop system to function to its full potential.
The cornerstone development of this self balancing device is the rigid connection of its pulleys, which allows it to maintain the correct belt tension irrespective of the direction of the load. It is an example of how challenging objectives can bring out the best from component manufacturers that need to work with VMs to find the best design solutions and which therefore defines them as world leaders in technology.
Aftermarket solutions
As an original equipment supplier of bespoke power transmission solutions, Dayco can be relied upon by the independent service and repair sector to deliver premium quality OE products, designed to fulfil the demands of the VMs.
Part of this commitment is the requirement to provide vehicle specific solutions, which means that, just like its traditional auxiliary belts which do not include a ‘universal, one size fits all’ option, its BSG belts are also of tailored design.
What this means for professional installers and workshops, is that they should dismiss the suggestion that a traditional auxiliary belt will be suitable for a BSG application. Should they do so, it’s likely to lead to premature belt failure and an unhappy customer.