Mann+Hummel explains why filter media, that is the material a filter is made from, is the heartbeat of a filter, and why all media is not equal.
Afilter is a filter, right? Whether it’s air, oil, fuel, cabin, hydraulic, they all stop contamination by filtering air or liquids through filter ‘paper’. So, this ‘paper’ (filter ‘media’ to give it its technical name) is largely the same then?
Well…yes and no. Irrespective of if the filter is a metal spin-on type for oil or fuel or a panel filter for air, the principle is largely the same. But the composition of this ‘media’ can differ significantly, even between similar part numbers and across different brands.
Filter media is usually the most expensive part of any filter. It is the hardest working part, subject to incredibly harsh conditions (heat, contaminant, water, cold, synthetic oils, bio-diesel etc) and is intended to last the whole service interval and not fail. The media has to be the precise specification per application: One-size-does-NOT-fit-all.
As a brief overview, there are common media types used in the automotive industry, all with differing properties required for different engines and uses.
- Cellulose media – plant-based, very common, one of the cheaper and easier types to manufacture.
Advantages include good dirt-holding capacity (service life), easy to pleat for common shapes (spin-on and elements), relatively bio-degradable with lower fossil fuel content.
Disadvantages can be a lower filter efficiency (especially for finer particles) and limited thermal resistance (i.e. not ideal for heavier-duty applications). Can degrade over time.
Cellulose media is hence often found in lighter applications such as cars/lower mileage.
- Mixed-fibre media – usually plant based with additional man-made material such as polyester or additives/resins.
Advantages include longer dirt-holding capacity verses cellulose-only, very good for liquid filter usage and with better thermal and chemical resistance, plus can be used multi-functionally (such as combined with hydrophobic coatings for water resistance).
Disadvantages can be higher cost, more complex manufacturing process, reduced biodegradability, higher quality control required due to complex nature.
Mixed fibre media is therefore often for applications requiring a longer life and usage with synthetic oils, i.e. longer service-life cars, LCVs and some heavier duty vehicles.
- Fully synthetic media – as it is named, a fully-synthetic filter media (polymer only).
Advantages are high filter efficiency (down to sub-micron levels), excellent wet strength compared to cellulose, excellent manufacturing consistency of the material, long service life.
Disadvantages can include higher manufacturing costs compared to cellulose and mixed-fibre, complexity of recycling after use, can require additional support within the filter assembly to avoid pleat collapse or deforming (i.e. use of a centre tube or frame etc).
Fully synthetic media is used for applications requiring high efficiency, service life and chemical resistance, such as HGVs, off-highway/heavy-duty and are often used in premium applications and cabin-air.
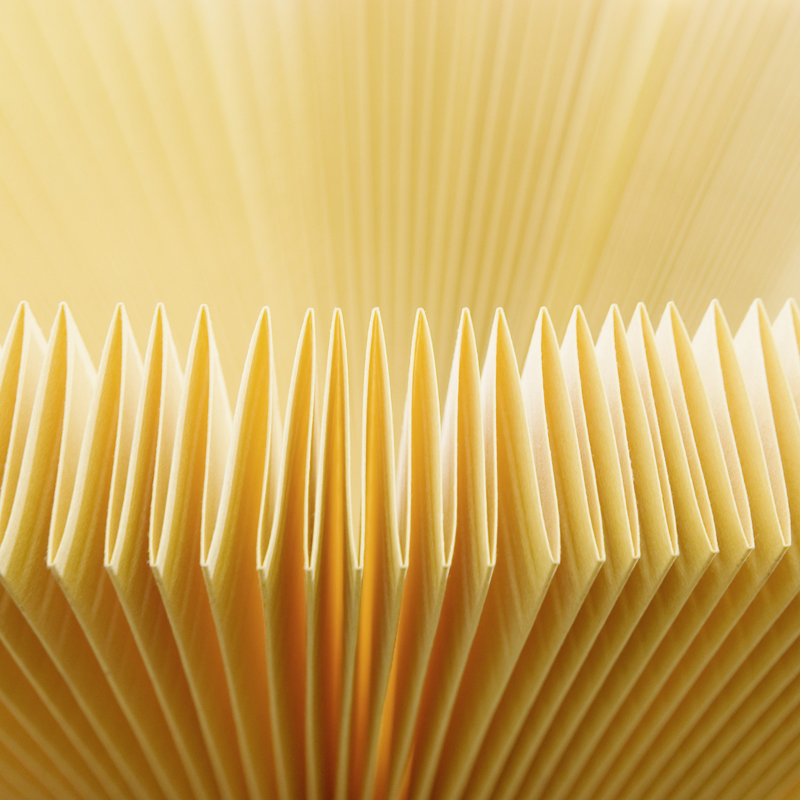

So, all of these factors and differences required and the cost involved means some filter brands cut corners with the media to allow for a lower price-point. To reduce cost, actions such as reducing media amount or using a lower-quality or specification media can shave a substantial amount of cost from a filter. When this is not openly visible (spin-on filter inside a can, or ‘strategically’ spaced-out pleats to give the impression of a larger area in air filters or elements) can be a smokescreen to hide lower performance compared to a quality (and more expensive) equivalent.
So, choose your filter brand wisely. Original Equipment manufacturers with years of experience, such as Mann+Hummel, have the science and understanding to provide the right filter, with the right media.